I have just published a book called The Re-Justification of God.
Here’s the cover:
 It is probably the ugliest book cover I have ever designed, but if you compare it with the cover from John Piper’s book on the right, you’ll see why I created the cover as I did.
It is probably the ugliest book cover I have ever designed, but if you compare it with the cover from John Piper’s book on the right, you’ll see why I created the cover as I did.
Why did I write The Re-Justification of God?
Ever since I read John Piper’s The Justification of God about twenty years ago, I have wanted to write a book in response called The Re-Justification of God.
Why?
I believe that Piper’s book does more to malign the name of God and His character than uplift and glorify it. To put it bluntly, I don’t think Piper’s book does anything to accomplish “The justification of God” but actually does the opposite!
So I wanted to write a book which explains Romans 9 in a way that presents God in light of Jesus Christ, in a way that does not make God responsible for hating Esau, hardening Pharaoh’s heart, and condemning a large majority of mankind to everlasting damnation in hell.
Look, I have great respect for John Piper, but much of his theology really gets my blood boiling, and this book of his on Romans 9 was no exception.
But it wasn’t just his book. Most of the explanations of Romans 9 I have read from Calvinists seem to be completely off track and do more to undermine the character of God than glorify it.
So in light of all the bad theology that has been taught from Romans 9, I wanted to write a book that explained the text of Romans 9 in a way that truly presents God in the light that Paul presents Him, as a God of light, love, mercy, grace, and longsuffering toward all.
That would be a great book, right?
Well, guess what?
Despite appearances, the book I just published is not that book. My The Re-Justification of God is not a point-by-point refutation of Piper’s The Justification of God. My book is not even a point-by-point refutation of the typical Calvinistic understanding of Romans 9. That is the book I set out to write, but it is not the book I am announcing here.
…Sorry to disappoint you.
However…
…My book IS the first draft in what will hopefully become that book.
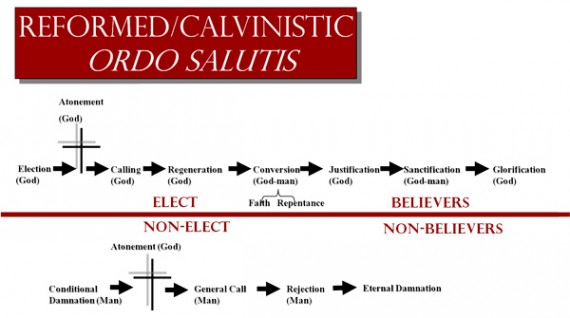
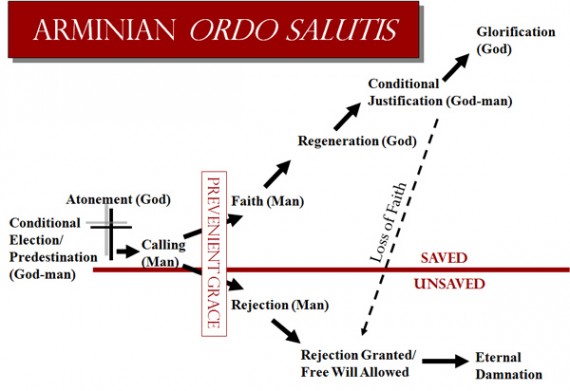
While I believe my new book does provide an overall big-picture analysis of Romans 9:10-24 that is neither Calvinistic nor Arminian, and while I believe my book provides logically and theologically sound explanations for why God “hated” Esau, why God hardened Pharaoh’s heart, and how God treats the “vessels of wrath” destined for destruction, I was not able to provide ALL the scholarly and exegetical details that a book like this requires.
So this book is the brief summary of the book I initially set out to write so many years ago. It is not finished, however. It is less than half-way done. Oh, the ideas are all there, but the book contains very little of the exegetical evidence which is needed to defend the ideas.
So why am I publishing this book now if it’s not done?
In the opening pages to this new book, I explain why, but in a nutshell, the reason is that if I didn’t publish it now, it would probably never get done. Also, having the book out there allows people to respond to it and interact with it so that in a future edition I can correct or attempt to better explain the ideas I present in the book.
And following the theme in the cover image above, here is an image of some of the edits I performed on this manuscript:

As with many of my books, there are probably still several typographic mistakes in it. If you find some, please send me an email, or use the “Contact Me” section on my About page to let me know where they are so I can correct these mistakes in future editions of the book.
So how can you get and read this book?
This book is available for purchase on Amazon.
Once you have read it, let me know what you think by leaving a review on Amazon.
And hey, would you let others know about this new book by using the share buttons below? Thanks!