
A Centered Set approach to church tries not to restrict anyone from participating. Sure, there are rules about how to participate, but in a Centered Set, since there are not boundaries, everybody by definition is “in.”
But what about the heretics? The really bad hell-bound heretics? The apostates and wicked men who lead people astray by lies and deceit? Cannot we at least restrict them?
Heretics Don’t Exist
Well, it may come as a surprise to learn that there is no such thing as a heretic. They are fictional creatures invented by religious leaders who want to scare people into strict compliance to everything the leader says. Like parents who try to scare their children into obedience by telling tales of the bogeyman, some church leaders try to scare their congregation with tales of fire-breathing heretics whose ideas originate in the pit of hell.
Scripture on Heresy
But doesn’t Scripture warn us about heresies? Yes, it does. More frequently than we realize.
The word heresy comes from the Greek word airesis, which is pronounced “heresies.” So the English word “heresy” is not a translation from the Greek, but is a transliteration, just like baptism (baptizō) and evangelism (euangelizō). Translators will often transliterate a Greek word when they are not fully sure how to translate it. They just take the Greek letters and change them into English letters, and call it good.
But it’s not so good for English readers who don’t know what’s going on behind the English. In the case of airesis, the translators knew what it meant, and most of the time, in most translations, it appears as “sect,” “division,” or “faction.”
Heresy in Acts
This is seen most prominently in Acts where Luke writes about the “sect (airesis) of the Sadducees” (5:17), the “sect (airesis) of the Pharisees” (15:5), and the “sect (airesis) of the Nazarenes” (24:5). We are generally familiar with the Pharisees and the Sadducees, but what was the “sect of the Nazarenes”? They were the followers of Jesus. They were Christians (cf. Acts 24:14; 26:5; 28:22).
So, according to Scripture itself, Christianity was one of the “heresies” at the time of the early church. This isn’t a bad thing. It is not a condemnation of Christianity. It is just a way of describing a group of people within the broader religion of Judaism. It refers to a group who had some different beliefs and practices than other groups within the big religious tent of Judaism.

Heresy in Paul
Outside of Acts, there are only three more uses of the word airesis. The first two are found in 1 Corinthians 11:19 and Galatians 5:20, and both refer to “divisions” and “factions” that occur within Christianity, and both teach that such divisions are destructive and damaging. Rather than divide over doctrine, we are to be unified in the Spirit. Neither use refers to some sort of pit-of-hell false teaching that must be condemned by the true spiritual leaders. To the contrary, both passages condemn the practice of forming divisions and splits (airesis) within the Body of Christ. Paul recognizes that genuine Christians can become divided, but he instructs that such practices are works of the flesh, and not a result of life lived in the Spirit.
If this understanding of these two passages is correct, the danger of airesis is not bad theology, but divisions within the Body of Christ. A fight against “heresy” is not a fight against bad doctrine, but against disunity in the church. Certainly, disagreements over doctrine can create division, but the proper response is not to separate from each other over our differences, but to love each other despite our differences.
We will will look at the final passage tomorrow, 2 Peter 2:1. But for now, what do you think of this idea of heresy? Maybe you think that the idea itself is heresy. If so, why? But if you disagree, be careful how you respond, for according to Scripture, divisiveness is the true heresy.




 But as church history and personal experience reveal, no church can completely guard the minds and hearts of the people who attend that church from different theology and dangerous ideas. To the contrary, it seems that the more a church tries to completely control what people hear, read, and think, the more cultish they become. And one of the defining characteristics of cults is that they are full of false teaching.
But as church history and personal experience reveal, no church can completely guard the minds and hearts of the people who attend that church from different theology and dangerous ideas. To the contrary, it seems that the more a church tries to completely control what people hear, read, and think, the more cultish they become. And one of the defining characteristics of cults is that they are full of false teaching.
 One of the primary reasons churches create doctrinal statements and other boundaries so so they can better protect the members against heresy and false teaching. Churches feel they need to separate the wheat from the chaff, the sheep from the wolves, the sound teacher from the false teacher, the orthodox from the heretic, and the righteous from the wicked.
One of the primary reasons churches create doctrinal statements and other boundaries so so they can better protect the members against heresy and false teaching. Churches feel they need to separate the wheat from the chaff, the sheep from the wolves, the sound teacher from the false teacher, the orthodox from the heretic, and the righteous from the wicked.
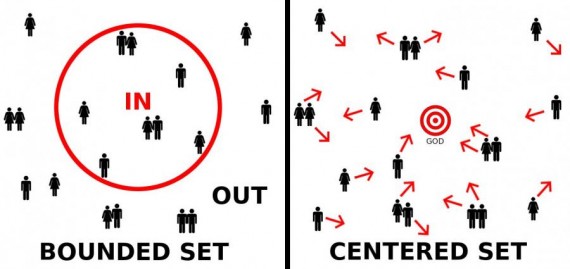
 I don’t think a Centered Set approach leads to universalism. To the contrary, I think a Centered-Set approach best reflects biblical theology.
I don’t think a Centered Set approach leads to universalism. To the contrary, I think a Centered-Set approach best reflects biblical theology.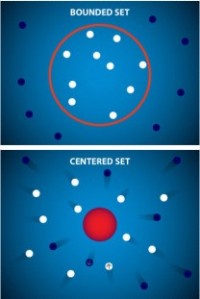
 One concept that really helps grasp the concept of living and ministering without doctrinal statements is idea of bounded and centered sets. This ideas was initially developed over 30 years ago by missiologist and anthropologist Paul Hebert in his book
One concept that really helps grasp the concept of living and ministering without doctrinal statements is idea of bounded and centered sets. This ideas was initially developed over 30 years ago by missiologist and anthropologist Paul Hebert in his book  If it helps, you can think of a bounded set as a Western style horse corral. The cowboys build the fence to keep the horses from wandering away. Outside the fence is where wild beasts and rustlers reside, just looking for a chance to kill or steal a horse.
If it helps, you can think of a bounded set as a Western style horse corral. The cowboys build the fence to keep the horses from wandering away. Outside the fence is where wild beasts and rustlers reside, just looking for a chance to kill or steal a horse.