The solution I proposed yesterday (and last year) about how to understand the violence of God in the Old Testament is based on the two theological convictions, the two ways of reading Scripture, and the two key passages which were discussed in earlier posts (see the link list at the bottom of this post).
Of primary importance, however, is the concept of reading the Bible backwards. If we are to understand what God was doing at the beginning parts of the Bible, we must read those parts in light of the end of the Bible. And by “the end” I do not mean the book of Revelation. Though Revelation may be found on the last pages of the Bible, the book of Revelation is not “the end” of the Bible.
What do I mean?
The Telos of the Bible
 In the New Testament, the Greek word telos is often translated “end,” but it could also be translated as “goal, purpose, or culmination.” So while the word can refer to the end of something chronologically, as in “then the end will come” (e.g., Matt 24:6, 14), it can also refer to the goal, purpose, or outcome of a series of events (cf. Rom 6:21-22).
In the New Testament, the Greek word telos is often translated “end,” but it could also be translated as “goal, purpose, or culmination.” So while the word can refer to the end of something chronologically, as in “then the end will come” (e.g., Matt 24:6, 14), it can also refer to the goal, purpose, or outcome of a series of events (cf. Rom 6:21-22).
One interesting use of the word in the New Testament, however, is in relation to Jesus Christ. There are numerous places which refer to Jesus Himself as the “end” (cf. Rom 10:4; 1 Cor 10:11; 15:24; Rev 21:6; 22:13).
This means that the goal, purpose, or culmination of God’s redemptive history is Jesus Christ. Jesus is what God has been working toward. Jesus is the fulfillment and completion of God’s eternal plan. Jesus is where all things have been headed. Jesus is the originator of history and is the light at the end of the tunnel of history.
So when I write about reading the Bible with the end in mind, I am thinking primarily about Jesus. We read the Bible with Jesus in mind. We read the Bible through Jesus-colored glasses.
The Telos of Jesus
With this in mind, there is one use of the word telos which I want to emphasize. It is found in Luke 22:37. Jesus is preparing His disciples for His crucifixion and His eventual departure from them, and says that the reason is because “this which is written about Me must still be accomplished in Me: ‘And He was numbered with the transgressors.’ For the things concerning Me have an end.” The word “end” Jesus uses there is telos.
Notice carefully what Jesus identifies as His end. He says that His end, His telos, His goal, His purpose, the culmination of His ministry, is that He be numbered with the transgressors. Jesus is saying that His goal, His purpose in coming, was to be identified as a transgressor—as a lawless, godless, sinner.
 This does not mean that Jesus was going to sin or become a sinner, but that it was necessary for Him to identify with us in our sin. His goal was to be counted among the lawless, the godless, and the transgressors. One translation of Luke 22:37 even states that Jesus’ goal was “let himself be taken for a criminal” (JB).
This does not mean that Jesus was going to sin or become a sinner, but that it was necessary for Him to identify with us in our sin. His goal was to be counted among the lawless, the godless, and the transgressors. One translation of Luke 22:37 even states that Jesus’ goal was “let himself be taken for a criminal” (JB).
Such an aspect of Christ’s ministry is sorely missing from most evangelical theology. Why would Jesus want to be counted among the lawless? Why would Jesus want to make it look like He was godless? Why was it the goal, the purpose, the telos of Jesus to be numbered among the transgressors?
Why?
Because Jesus is the ultimate and complete revelation of God, and this is what God has been doing from the very beginning.
By counting Himself among the transgressors, Jesus reveals to us once and for all what God has been doing all along. Jesus is not guilty, but to the outside observer, He looked guilty. To those who did not know better, as Jesus hung on the cross, He looked like a traitor, a thief, a common criminal dying on a cross.
So also with God.
To those who do not have eyes to see, to those who do not peer behind the curtain, to those who do not see read Jesus back into the pages of the Old Testament, God looks insanely guilty. God looks like the greatest traitor, thief, and criminal of the universe. Is God guilty of these things? He is not. No more than Jesus was guilty as He hung on the cross. But God looks guilty, because, just like Jesus, God was numbering Himself among the transgressors. God looks violent in the Old Testament in the same way that Jesus looks like a criminal when He hung on the cross.
Why would God do this? For the same reasons Jesus did: to free us from sin, death, and the devil. To destroy the destroyer’s work. To liberate us from bondage and decay. To reconcile us to Himself. To redeem a fallen world. To take the blame for that which would otherwise have sent humanity into an ever-increasing spiral of destructive violence.
 How can a God who says "Love your enemies" (Matthew 5:44) be the same God who instructs His people in the Old Testament to kill their enemies?
How can a God who says "Love your enemies" (Matthew 5:44) be the same God who instructs His people in the Old Testament to kill their enemies?
These are the sorts of questions we discuss and (try to) answer in my online discipleship group. Members of the group can also take ALL of my online courses (Valued at over $1000) at no charge. Learn more here: Join the RedeemingGod.com Discipleship Group I can't wait to hear what you have to say, and how we can help you better understand God and learn to live like Him in this world!





 The first is Romans 1:2, but there the word Paul uses for “holy” is hagiais instead of the normal word for divine holiness, hierais. The same usage applies to Romans 7:12 where Paul speaks of the “holy law.”
The first is Romans 1:2, but there the word Paul uses for “holy” is hagiais instead of the normal word for divine holiness, hierais. The same usage applies to Romans 7:12 where Paul speaks of the “holy law.” 

 When most people ask this question, they are primarily referring to the “400 years of silence” in between Malachi and Matthew. I will try to explain what was going on during those years, but really, the question of God’s so-called “years of silence” is much more complex.
When most people ask this question, they are primarily referring to the “400 years of silence” in between Malachi and Matthew. I will try to explain what was going on during those years, but really, the question of God’s so-called “years of silence” is much more complex.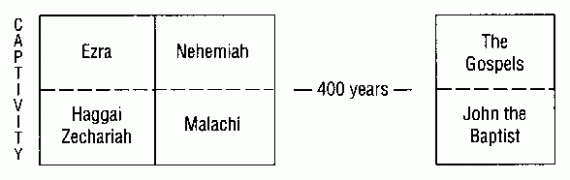
 But God’s apparent silence throughout most of history is not because God was absent or inactive, but simply because it takes eyes of faith to see where God is at work even when He doesn’t have someone write about it.
But God’s apparent silence throughout most of history is not because God was absent or inactive, but simply because it takes eyes of faith to see where God is at work even when He doesn’t have someone write about it.
 (As long as I am off in the weeds writing about scholarly conventional wisdom which I do not accept, I might as well include here that I also do not accept most of the canons of textual criticism which give priority to the Critical Text based on a few early documents rather than the Majority Text based on thousands of later documents…)
(As long as I am off in the weeds writing about scholarly conventional wisdom which I do not accept, I might as well include here that I also do not accept most of the canons of textual criticism which give priority to the Critical Text based on a few early documents rather than the Majority Text based on thousands of later documents…)
 This post on Jesus’ parables is part of the August
This post on Jesus’ parables is part of the August  In other words, Jesus told parables to mask the truth, to hide it, to cloak it, to make it unclear. Jesus’ parables are supposed to be confusing! He wanted them to be confusing!
In other words, Jesus told parables to mask the truth, to hide it, to cloak it, to make it unclear. Jesus’ parables are supposed to be confusing! He wanted them to be confusing!